PCB
Various types of PCBs (single-sided, double-sided, FPCB, BUILD-UP, R/F, METAL-PCB, CERAMIC-PCB, etc.) can be produced. Completed the construction of a total solution that can meet the delivery date through partners.
Section

It is a low-cost product with a low component and mounting density, a circuit formed on only one side of the board, and a short manufacturing period.

Both sides

The circuit is formed on both sides, and it looks like two single-sided boards are attached. The advantage of double-sided PCB is that it can increase the density of parts and circuits than single-sided PCBs.

MULTI-LAYER

In the case of a MULTI-LAYER PCB, that is, a multilayer PCB, components are mounted on both sides and each layer contains a circuit. High-density component mounting is possible, and there are advantages such as product miniaturization and short circuit distance (EMI reduction). It has the disadvantage that the production cost is high and it is difficult to change the internal circuit.

FPCB

Using polyimide, a soft material, as its main raw material, it is widely used for miniaturization and weight reduction of electronic products. It has strong heat resistance, curvature resistance and chemical resistance. It has the advantage of enabling 3D wiring by using the curvature-resistant property.

RIGID FLEXIBLE PCB
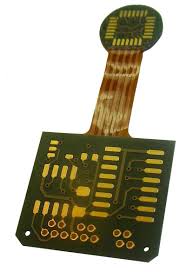
It is a product that combines the advantages of the ductility of FPCB and the rigidity of RIGID. It is a product with easy SMT mounting and partial flexibility.

METAL PCB
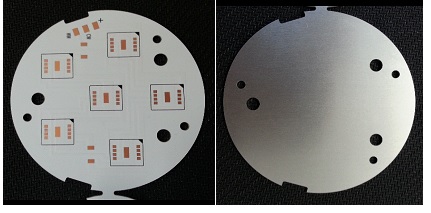
The insulating layer uses a material called heat dissipation T-PLUG that does not allow electricity to flow and has good thermal conductivity. Heat conduction is fast and heat dissipation is easy, so it is applied to LED related products

CERAMIC PCB
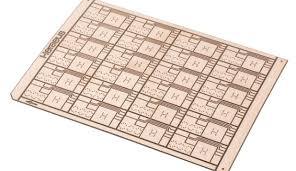
It has excellent heat resistance, low dielectric constant, and low dielectric loss. The advantage is that it is very stable and reliable in high temperature and high humidity.

SMT

1. Loader
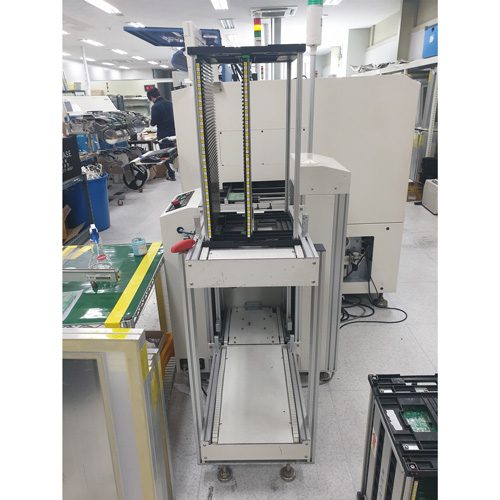

The process of automatically flowing the magazine’s board into the line

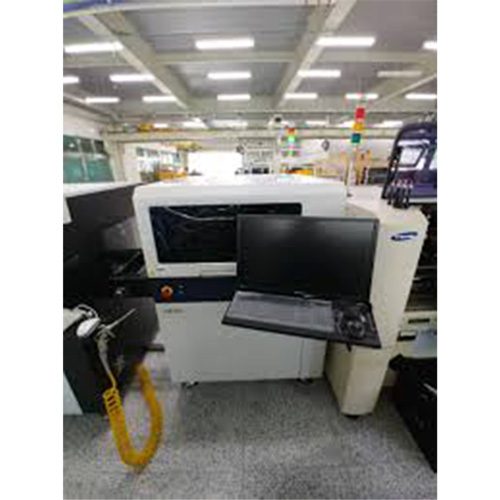
2. Screen printer

Process of applying SOLDER CREAM on the PCB using METAL MASK

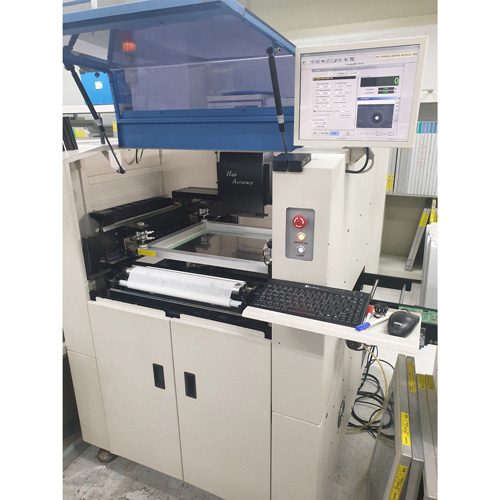
3. solder paste inspection

The process of inspecting the volume condition of SOLDER CREAM applied to the PCB

4. Chip Mounter
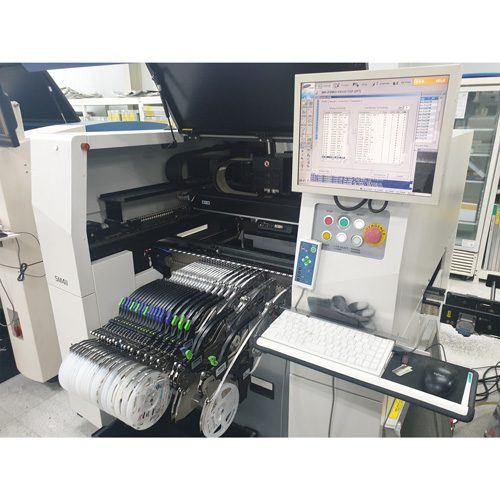

Process of mass-mounting mainly small chip on PCB coated with SOLDER CREAM

5. Multi-mounter
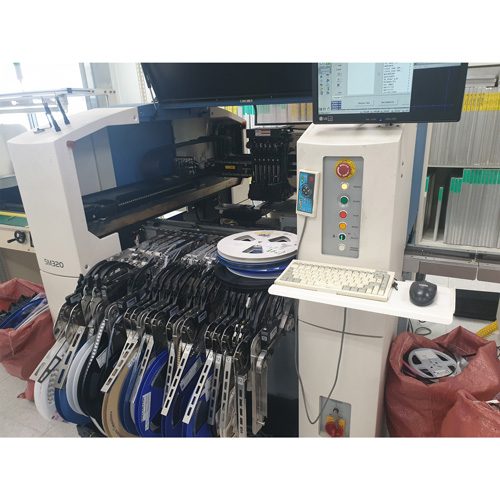

The height and size of the parts are larger than the general chip and the process of mounting expensive parts such as BGA or parts with various shapes

6. Reflow
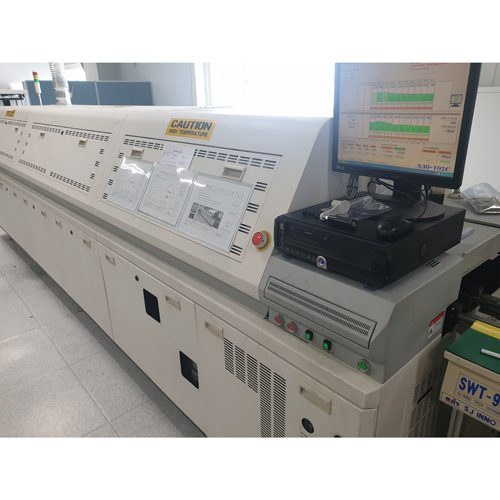

Process of melting and hardening the solder cream by applying high temperature heat and N2 to the PCB on which the parts are mounted

7. Un loader
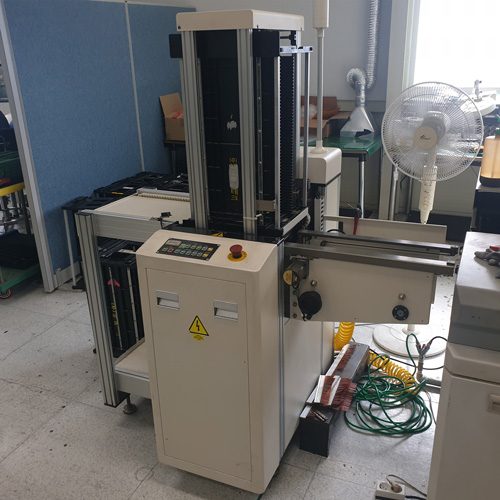

The process of storing the line board in the magazine

8. AOI
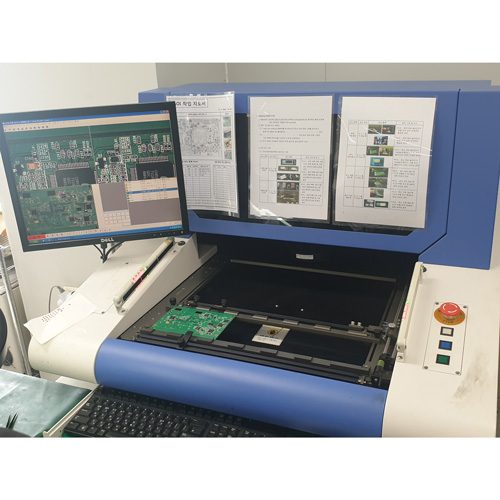

Automatic optical inspection

